Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Identify and change unhelpful thought patterns that lead to negative emotions and behaviors, so you can handle challenges better in daily life.
Core Concept
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that aims to reduce symptoms of various mental health conditions, primarily depression, and disorders such as PTSD and anxiety disorders. This therapy focuses on challenging unhelpful and irrational negative thoughts and beliefs, referred to as ‘self-talk’ and replacing them with more rational positive self-talk. This alteration in a person’s thinking produces less anxiety and depression. It was developed by psychoanalyst Aaron Beck in the 1950’s.
CBT looks at how your thoughts, physical feelings, emotions and behaviors are all interlinked and have an impact on each other.
Key concepts in CBT include “cognitive distortions”, “automatic thoughts”, and “behavioral activation”.
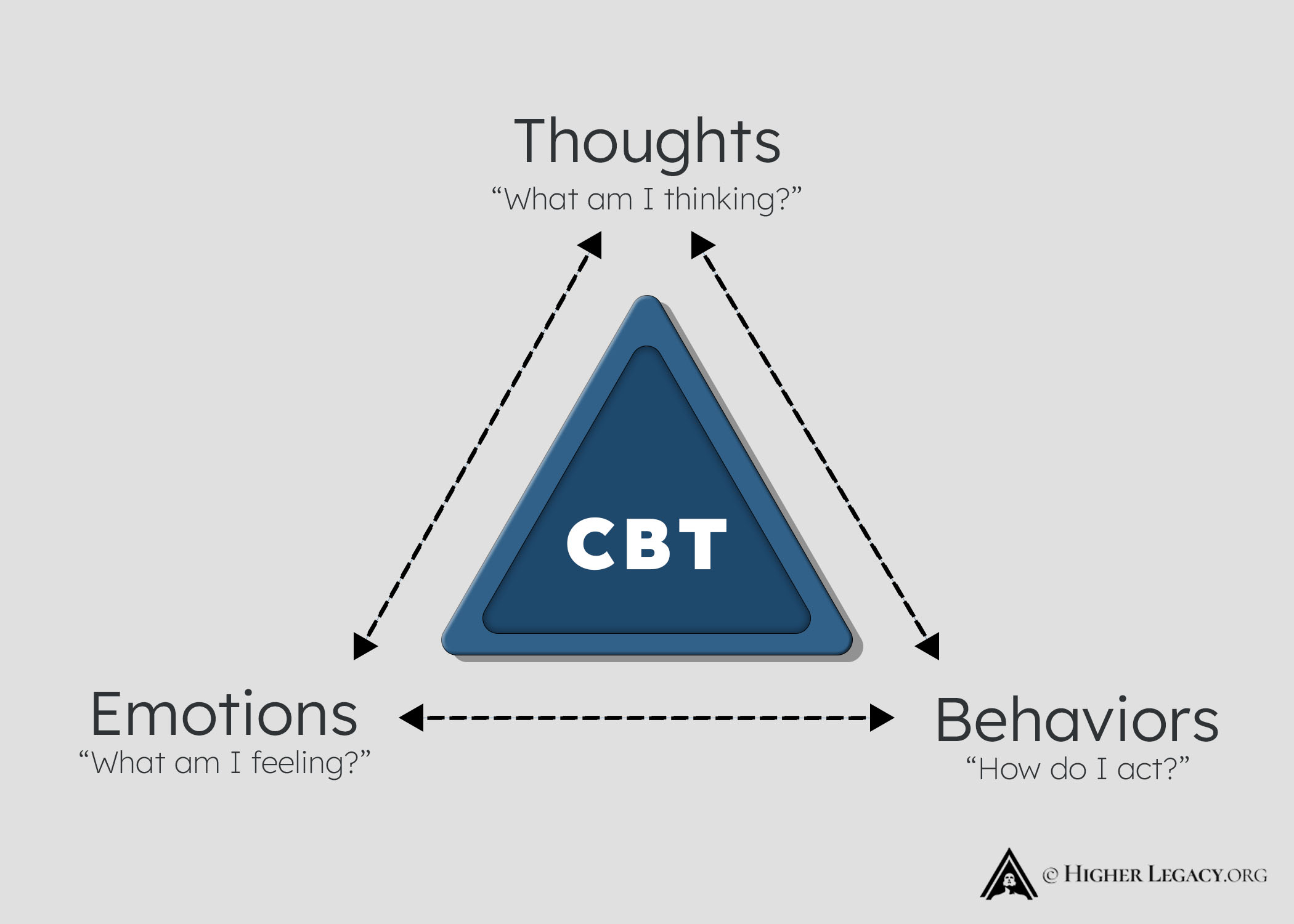
How It Works:
- Preparation and Safe Space
- Orient and Assess the Issue
- Set a Simple Goal or Agenda
- Cycle Through Thoughts, Emotions, Behaviors
- Create a plan of action
- Reflection and Self-Care
Optional: Download CBT Worksheet
Self-Applied CBT Exercise:
- [CBT Exercise here]
[Related quote here]